Although it reminds of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis does not create the characteristic RA antibodies. A negative rheumatoid factor test result helps to distinguish psoriatic from rheumatoid arthritis. Psoriatic arthritis attacks about 10% of the people suffering from psoriasis. Psoriatic arthritis can develop at any moment regardless of age, but it usually develops in people between 30 and 50, in which, it seems, hereditary factors play a considerable role in increasing the risk of the disease.
Pseudogout
Pseudogout: Disease of the elderly
This disease is similar to gout, but it is caused by various crystals – in this case Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals which are usually formed with no cause whatsoever. Pseudogout is common among the elderly, it affects around 3 % of people in their sixties and as much as 50% of all people over 90.
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia - the pain is real
If literally "everything hurts", you may be suffering from fibromyalgia (FM) - one of the most tormentous health conditions. One of the newer textbooks describes FM as "a chronic, poorly explained condition which incapacitates." It is all that and much more.
Fibromyalgia is relatively common, more that a million UK citizens are suffering from it which makes up 2 percent of the whole population. The great majority of patients suffering from FM - more than 90 percent - are women, and the condition usually starts upon the person entering their mid-forties. Fibromyalgia is a significant medical issue which encompasses 20 percent of all rheumatologists visits..
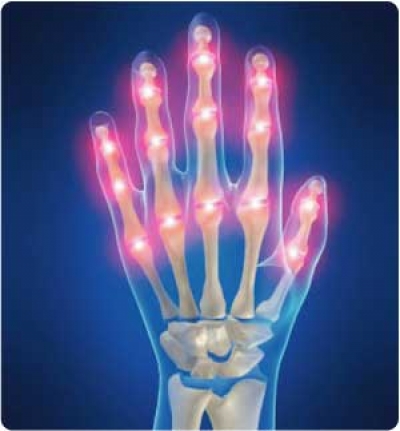
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthrosis and rheumatism
The World Health Organisation (WHO) defines the concept of rheumatism as all conditions (about 450 different ones) which are manifested in the musculoskeletal system and which are associated with pain and limited movability. All these conditions are almost always chronic and are usually not curable. They are divided into four main groups:
- Inflammatory rheumatic diseases, i.e. arthritis
- Degenerative changes in the joints, i.e. arthrosis
- Rheumatism of the soft tissue, i.e. fibromyalgia
- Conditions of the metabolism which affect the joints, i.e. gout
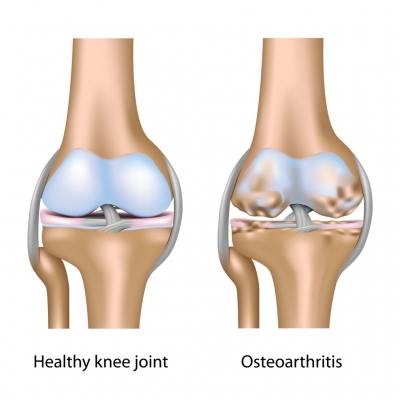
Osteoarthritis
What is osteoarthritis?
The word arthritis comes from the Greek "Arthro-" which means joint, and,-ose "or" osis "meaning illness, disease. Here we are talking about lesions in one or more joints that do not always begin with cartilage damage and are not primarily induced by inflammation. There are many factors that cause or favor damaging of the cartilage. In the beginning it often encompasses incorrect burdening of a particular joint or its overload. However, congenital defects and accidents can also lead to premature wear-out of the cartilage. Being as the process, once started, without treatment continually progresses, we have as a consequence total diminishing of the cartilage layer and deformation of the bone situated beneath that cartilage, as well as changes to the mucosa which the joint is lined with.